1. Definition - OLEDoS
Silicon based OLED, an OLED based on single crystal silicon, is called OLED on Silicon in English, so it is called OLEDoS in the industry.
What is OLED?
OLED is the abbreviation of Organic Light Emitting Diode, which can generate light and produce display screens through organic materials. Compared with traditional liquid crystal display technology, OLED has self luminous characteristics, and each OLED pixel can emit light independently without backlight.
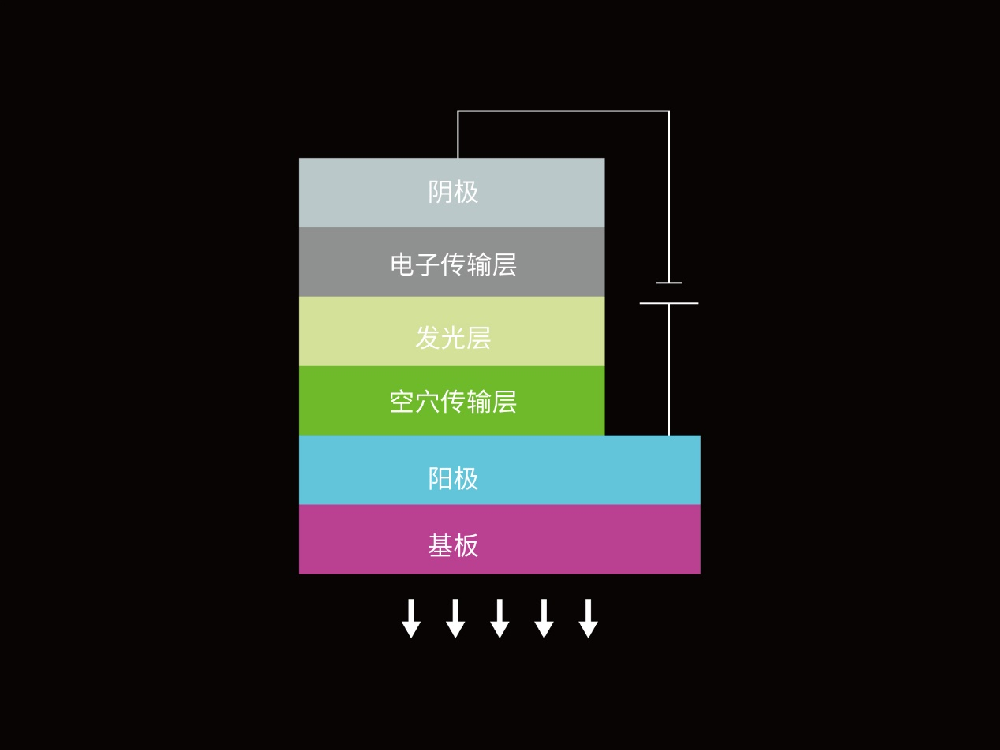
Figure 1: OLED structure diagram
Because each pixel can be controlled independently, OLED can achieve high contrast and true black. When a pixel does not need to emit light, the current can be turned off to completely turn off the light. This is different from LCD which needs backlight to control the light transmission.
The self illumination of OLED also brings other advantages, such as faster response time, wider viewing angle and lower power consumption. Fast response time means smoother image switching, which is very important for fast moving scenes or game players. Wide viewing angle means that color and brightness can remain stable even when viewing angle changes. For electronic equipment, the ideal state is to achieve high performance with low power consumption. Energy saving is also a necessary requirement. Therefore, OLED is widely used in smart phones, televisions and other displays.
But different from traditional TFT-OLED displays, silicon based OLEDs use single crystal silicon as the substrate, and CMOS driver circuits are integrated in the single crystal silicon.
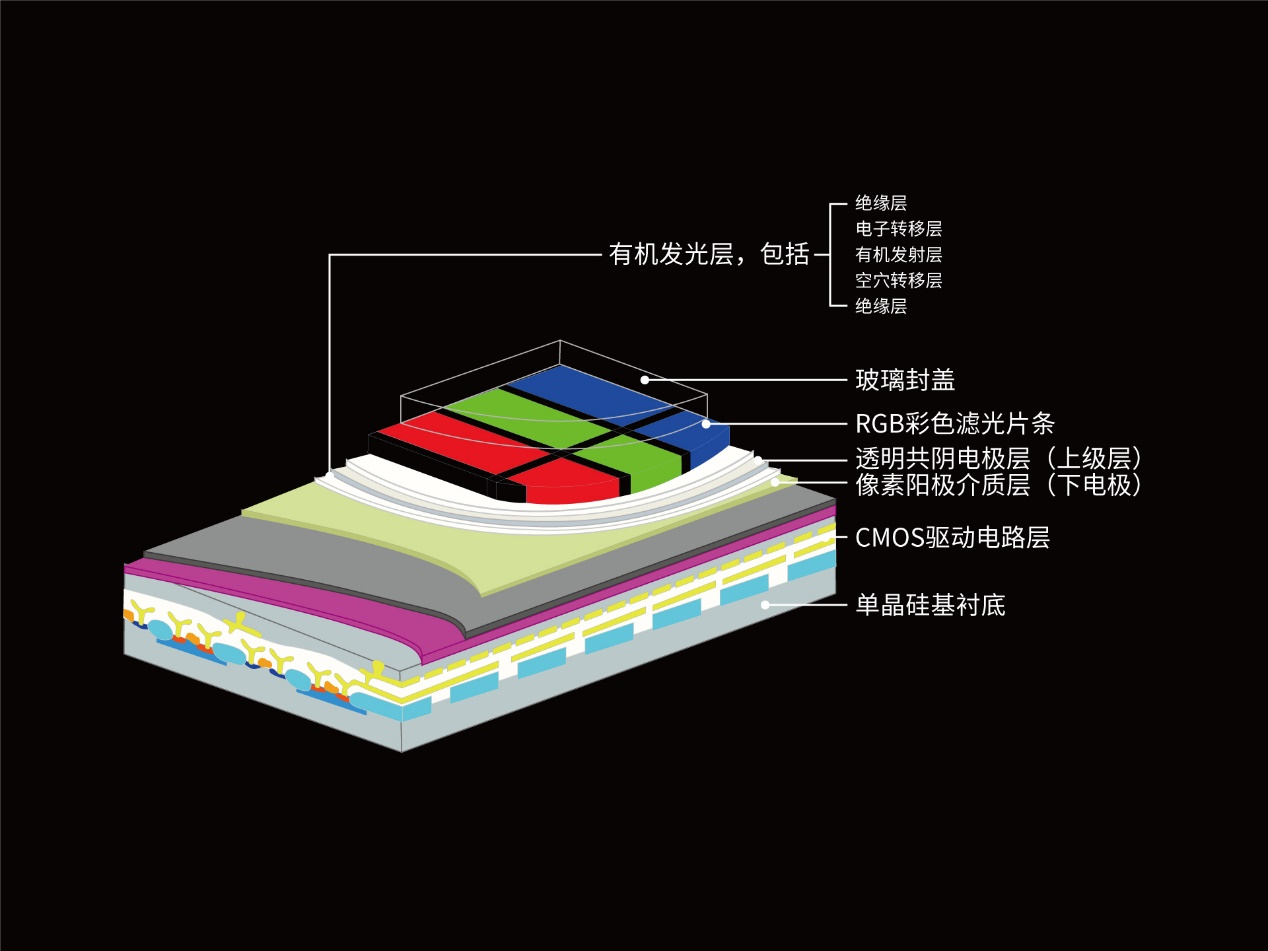
Figure 2: OLEDOS structure diagram
Silicon based OLEDs directly place pixels on silicon wafers instead of glass substrates. The pixel size can be smaller and the pixel density can be higher. Generally, the pixel density of an ordinary display is about hundreds of pixels per inch, while a silicon based OLED can provide a high pixel density of thousands of pixels per inch. While arranging a large number of pixels, it keeps the physical size small and precise, so that it can display on a stamp size chip with a resolution no less than 4K TV.

Figure 3: Comparison between Conventional pixel arrangement and OLEDoS pixel arrangement
2. Form Micro OLED
From the perspective of morphology, silicon based OLED is an OLED micro display, so it is called micro OLED in the industry.
Compared with the common LCD, OLED, LED and other large and medium-sized display panels, the micro display is a special product form, usually the diagonal size of the screen is less than 40mm.
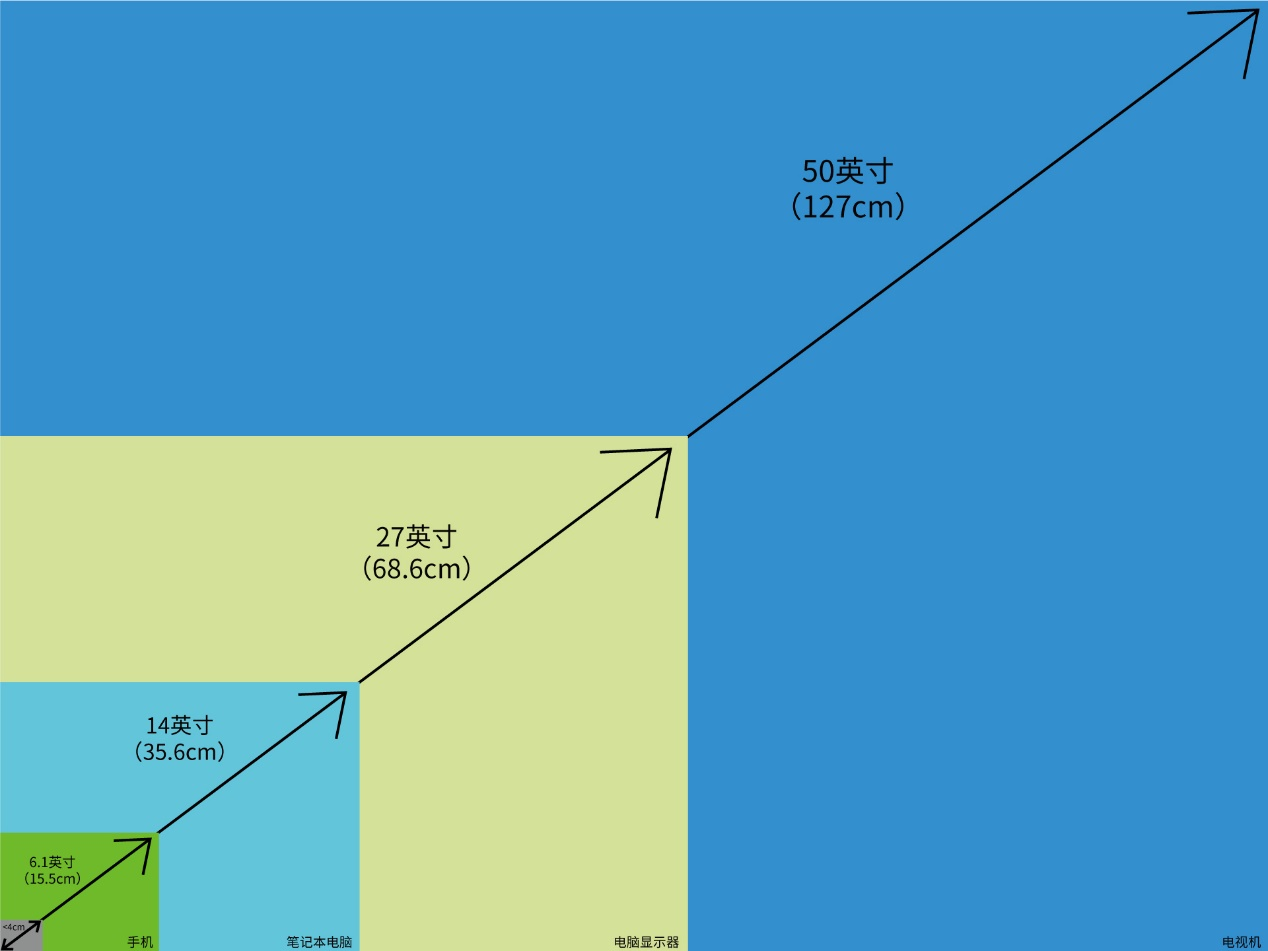
Figure 4: Diagonal comparison diagram of TV/PC/mobile phone/micro display
The physical size of micro display itself is small, and it can not be viewed directly, but it can form a large screen display through the optical system, so it is widely used in projector, near eye display and other fields.
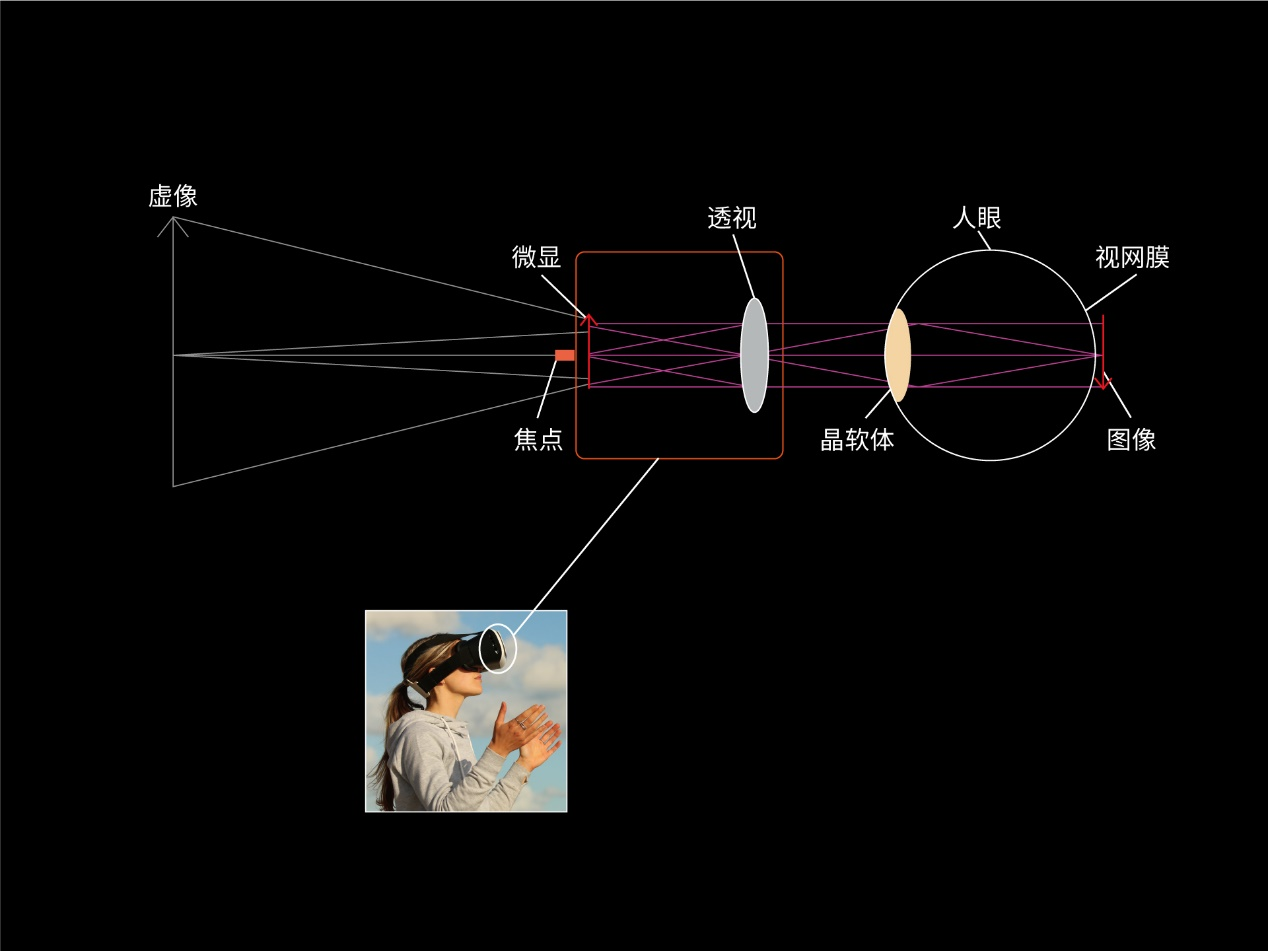
Figure 5: Near eye display imaging diagram
3. Application - near eye display
Micro OLED retains many advantages of OLED display screen, and has the potential of higher resolution than traditional OLED, so it is different from other applications of traditional OLED.
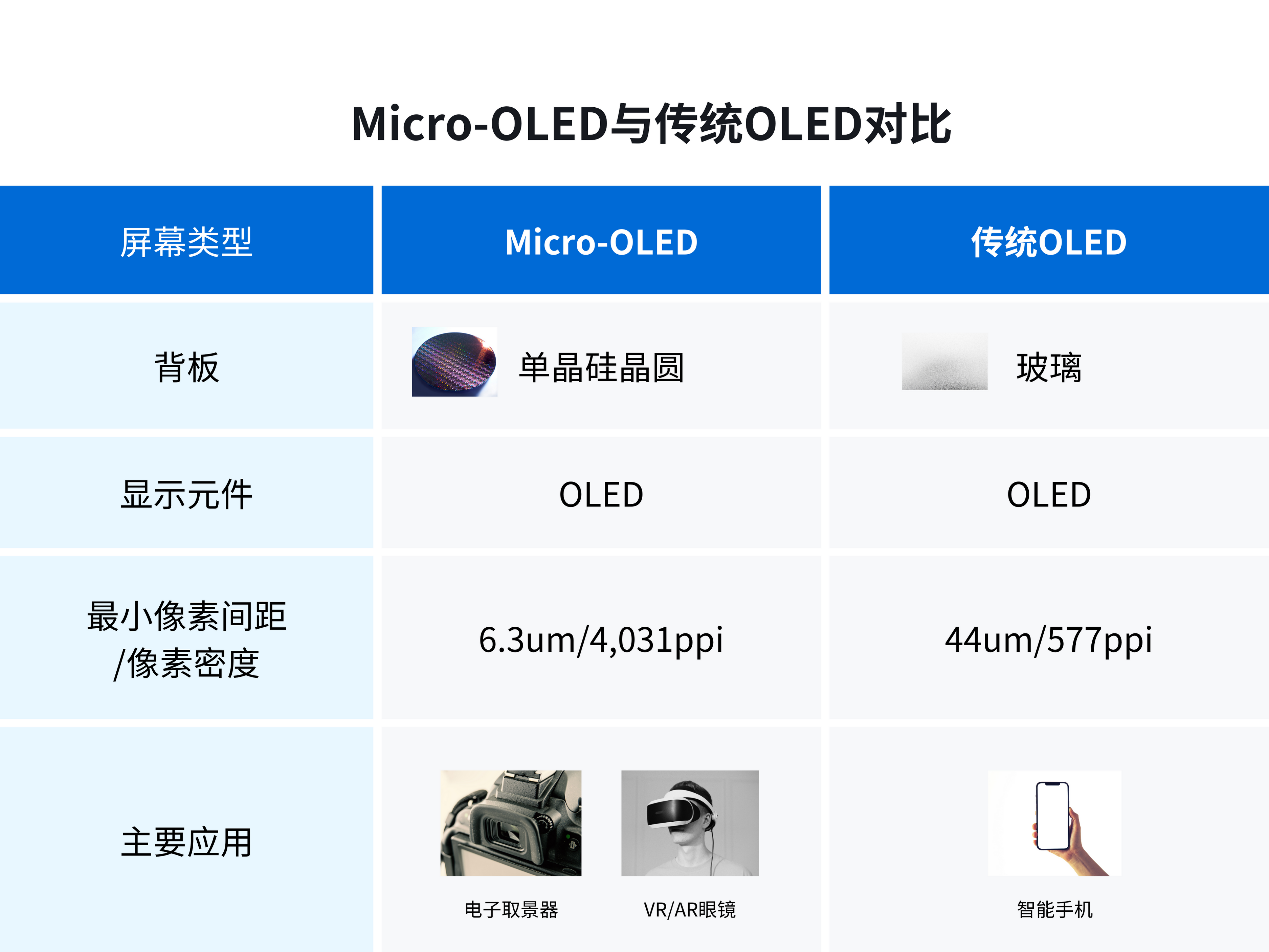
Figure 6: Comparison between Micro OLED and traditional OLED
The mobile phones we use and the televisions we watch do not appear unclear, and the visible resolution is not low. Why does the near eye display need to look for a display technology with higher pixel density?
The key lies in "near eye". For general mobile phone and TV viewing, there is usually a long distance from the screen. At this time, the display technology with low pixel density can provide sufficient clarity. However, when we use near eye display devices such as VR glasses, the display technology of low pixel density will lead to the phenomenon that the pixels are obviously visible and blurred after the image is magnified, because this type of display technology does not have the ability to significantly compress the size of pixels in a limited physical size, resulting in insufficient pixel points on the micro display to support the display of clear images.

Figure 7: Traditional technology has obvious graininess
In life, we will find that the image of the screen with lower resolution looks clearer when viewed from a distance. However, if you place your eyes close to the screen, it is easy to see the pixel border. This is because the number of pixels in the field of view decreases as the distance decreases. For near eye display, it is more necessary for the display to have a higher pixel density, so that more pixels are arranged in a limited space. When the eyes are close to the screen, there are enough pixels in the field of view.
In addition, from the perspective of vision, the resolving power of the human eye is not constant, but related to the ambient brightness. When the brightness is too low, the resolving power decreases, but when the brightness is too high, it will also cause "dazzling", not the brighter the better. The resolving power of the human eye is also related to the relative contrast of the observed scene. When the relative contrast is small, the brightness of the scene and the background is very close, and the resolving power of the human eye will decline.
Silicon based OLED micro display can provide higher pixel density, appropriate brightness and contrast for the head display main display, fully improve the visual field clarity and experience immersion, thus becoming the mainstream of near eye display field.
4. Comparison - commercialization prospect
In order to have a deeper understanding of silicon based OLEDs, we can also put them in the "same kind" group to observe.
According to different light-emitting principles, micro displays can be divided into digital micro mirror devices (DMD), liquid crystal on silicon (LCOS) micro displays, LCD micro displays, OLED micro displays (silicon OLED), LED micro displays and other major types.
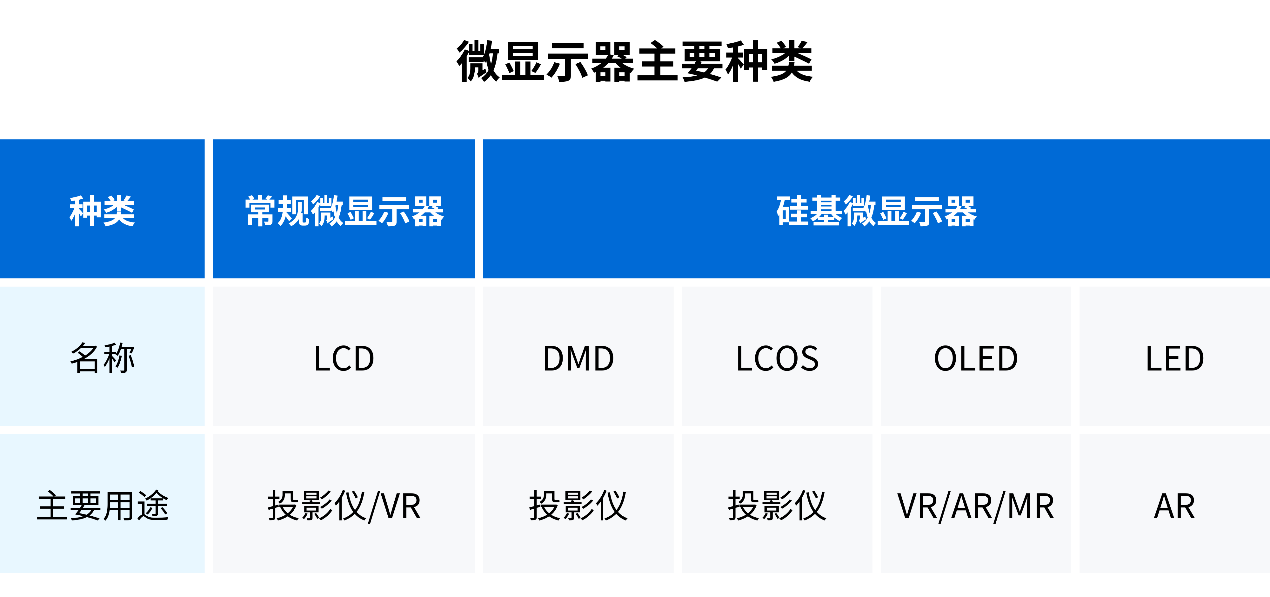
Figure 8: Main types of micro displays
LCD micro display, OLED micro display and LED micro display are all suitable for near eye display, but they also have advantages and disadvantages.
(1) From the perspective of performance and wearability, the advantages of silicon based OLED are greater than fast LCD (blue area in the table below):
·Fast LCD requires a backlight. The system is large in size, limited in brightness and contrast, low in luminous utilization, high in system loss and power consumption;
·Fast LCD is also an LCD with large pixel pitch, which is not conducive to further improving the resolution and is bound to be eliminated from the market.
(2) From the perspective of industrialization process, the mass production capacity of silicon based OLED is higher than micro LED (orange area in the table below):
·Micro LED has high luminous efficiency and can produce millions of nits of brightness, but there are bottlenecks such as massive transfer and full-color, and its industrialization is extremely immature.
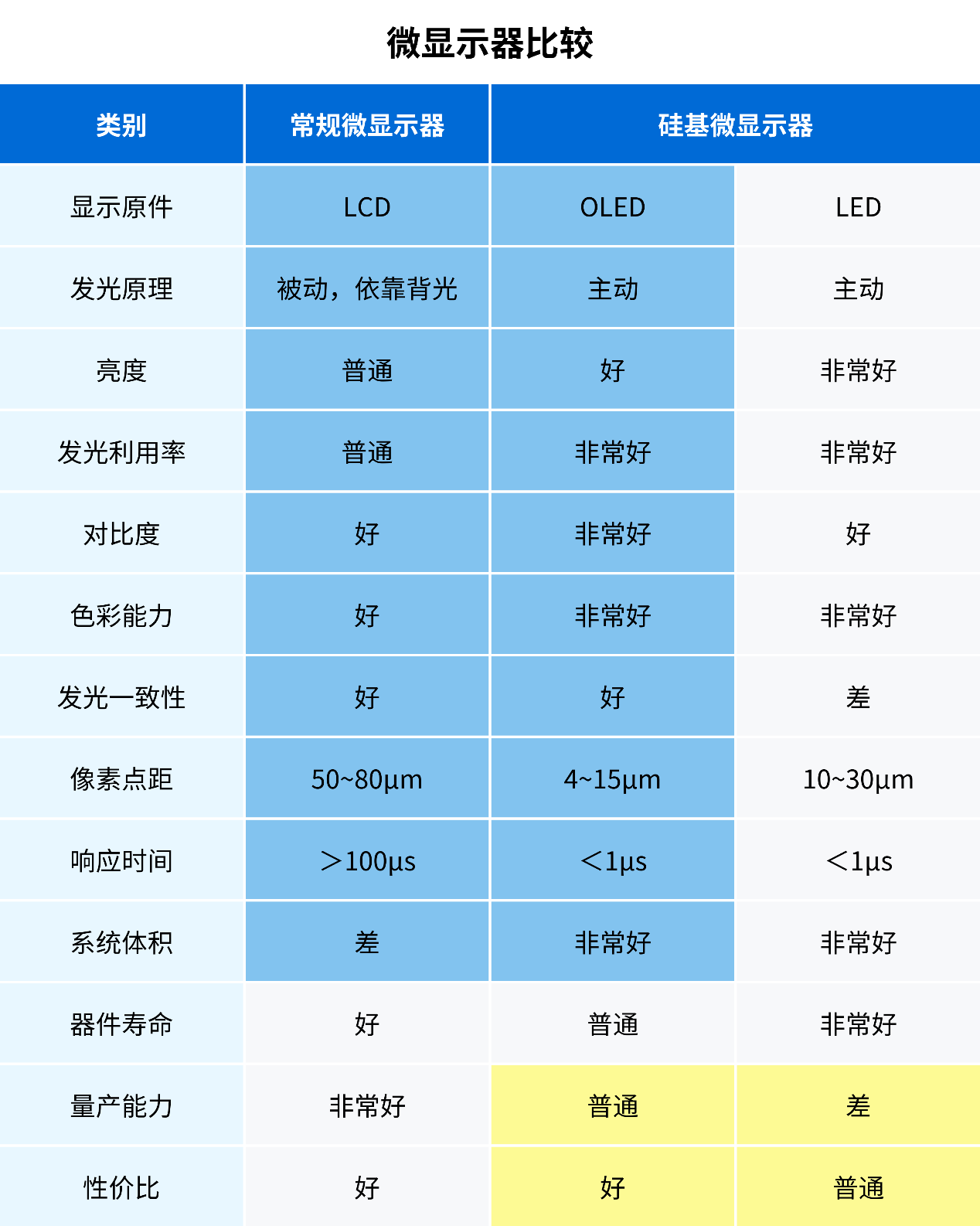
Figure 9: Performance parameters and cost performance comparison of mainstream trend micro displays
Although micro LED has the advantages of brightness and longevity, the intelligent head display takes VTS as the mainstream path and belongs to the consumer electronics market, so there are no strict requirements on brightness and longevity. It can be seen that micro OLED has a bright prospect of commercialization.
Summary
Silicon based OLED is a miniaturized OLED technology (Micro OLED). Different from the typical large size OLED screen, it uses a single crystal silicon backplane (OLEDoS), with extremely high pixel density, which is conducive to further improving the resolution and is suitable for near eye display. Compared with traditional LCD screens, silicon based OLEDs have the advantages of high PPI, high contrast, high response speed, wide viewing angle and low power consumption; At the same time, its technology is mature and its industry is booming. It has a huge commercial development prospect in the field of intelligent head mounted displays.













